Generates the basis matrix of regular M-spline, periodic M-spline, and the corresponding integrals and derivatives.
Usage
mSpline(
x,
df = NULL,
knots = NULL,
degree = 3L,
intercept = FALSE,
Boundary.knots = NULL,
periodic = FALSE,
derivs = 0L,
integral = FALSE,
warn.outside = getOption("splines2.warn.outside", TRUE),
...
)
msp(
x,
df = NULL,
knots = NULL,
degree = 3L,
intercept = FALSE,
Boundary.knots = NULL,
periodic = FALSE,
derivs = 0L,
integral = FALSE,
warn.outside = getOption("splines2.warn.outside", TRUE),
...
)Arguments
- x
The predictor variable. Missing values are allowed and will be returned as they are.
- df
Degree of freedom that equals to the column number of the returned matrix. One can specify
dfrather thanknots, then the function choosesdf - degree - as.integer(intercept)internal knots at suitable quantiles ofxignoring missing values and thosexoutside of the boundary. For periodic splines,df - as.integer(intercept)internal knots will be chosen at suitable quantiles ofxrelative to the beginning of the cyclic intervals they belong to (see Examples) and the number of internal knots must be greater or equal to the specifieddegree - 1. If internal knots are specified viaknots, the specifieddfwill be ignored.- knots
The internal breakpoints that define the splines. The default is
NULL, which results in a basis for ordinary polynomial regression. Typical values are the mean or median for one knot, quantiles for more knots. For periodic splines, the number of knots must be greater or equal to the specifieddegree - 1. Duplicated internal knots are not allowed.- degree
A nonnegative integer specifying the degree of the piecewise polynomial. The default value is
3for cubic splines. Zero degree is allowed for piecewise constant basis functions.- intercept
If
TRUE, the complete basis matrix will be returned. Otherwise, the first basis will be excluded from the output.- Boundary.knots
Boundary points at which to anchor the splines. By default, they are the range of
xexcludingNA. If bothknotsandBoundary.knotsare supplied, the basis parameters do not depend onx. Data can extend beyondBoundary.knots. For periodic splines, the specified bounary knots define the cyclic interval.- periodic
A logical value. If
TRUE, the periodic splines will be returned. The default value isFALSE.- derivs
A nonnegative integer specifying the order of derivatives of splines basis function. The default value is
0.- integral
A logical value. If
TRUE, the corresponding integrals of spline basis functions will be returned. The default value isFALSE. For periodic splines, the integral of each basis is integrated from the left boundary knot.- warn.outside
A logical value indicating if a warning should be thrown out when any
xis outside the boundary. This option can also be set throughoptions("splines2.warn.outside")after the package is loaded.- ...
Optional arguments that are not used.
Value
A numeric matrix of length(x) rows and df columns if
df is specified. If knots are specified instead, the
output matrix will consist of length(knots) + degree +
as.integer(intercept) columns if periodic = FALSE, or
length(knots) + as.integer(intercept) columns if periodic =
TRUE. Attributes that correspond to the arguments specified are
returned for usage of other functions in this package.
Details
This function contains an implementation of the closed-form M-spline basis
based on the recursion formula given by Ramsay (1988) or periodic M-spline
basis following the procedure producing periodic B-splines given in Piegl
and Tiller (1997). For monotone regression, one can use I-splines (see
iSpline) instead of M-splines. For shape-restricted
regression, see Wang and Yan (2021) for examples.
The function msp() is an alias of to encourage the use in a model
formula.
References
Ramsay, J. O. (1988). Monotone regression splines in action. Statistical science, 3(4), 425–441.
Piegl, L., & Tiller, W. (1997). The NURBS book. Springer Science & Business Media.
Wang, W., & Yan, J. (2021). Shape-restricted regression splines with R package splines2. Journal of Data Science, 19(3),498–517.
Examples
library(splines2)
### example given in the reference paper by Ramsay (1988)
x <- seq.int(0, 1, 0.01)
knots <- c(0.3, 0.5, 0.6)
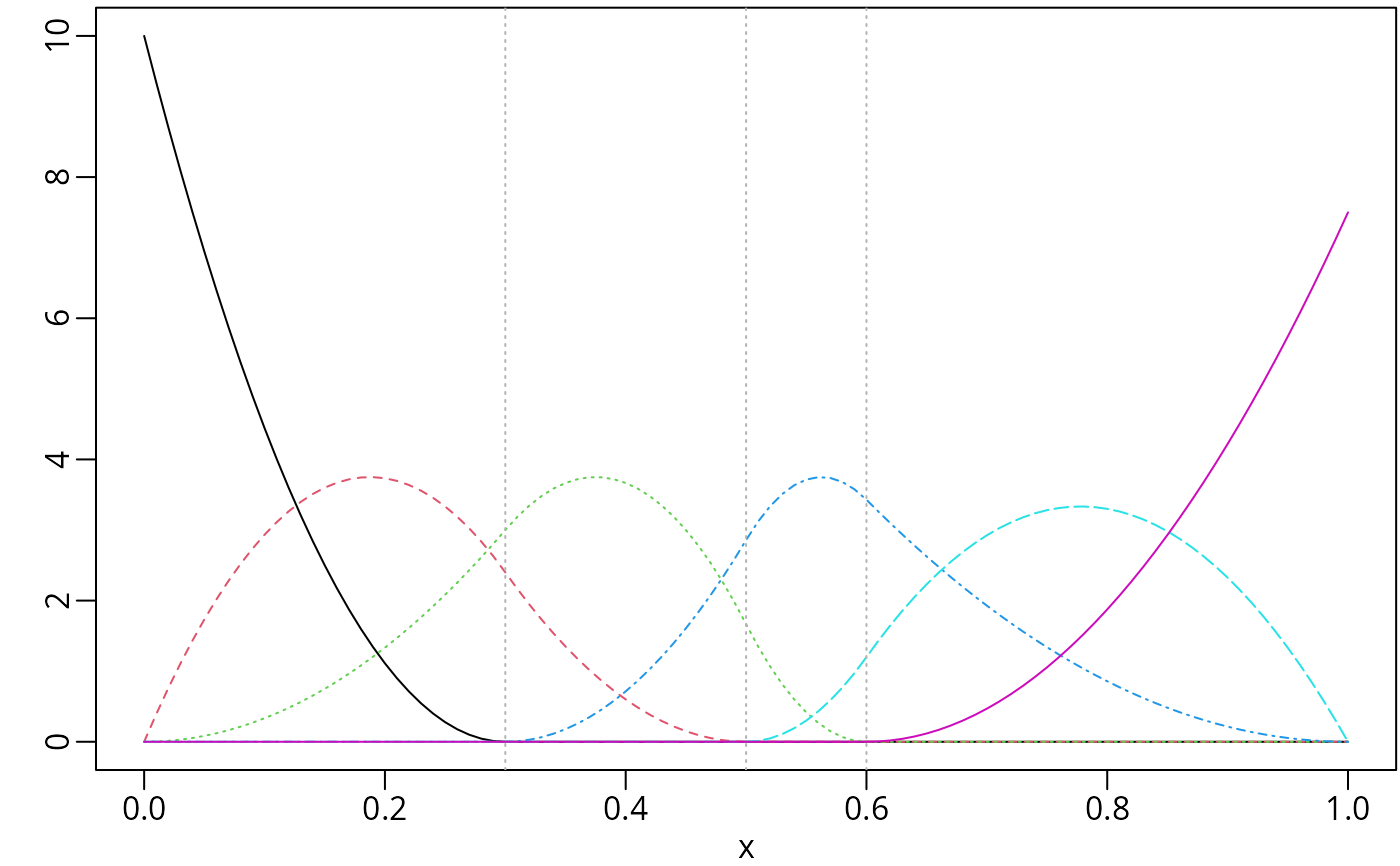
msMat <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 2, intercept = TRUE)
op <- par(mar = c(2.5, 2.5, 0.2, 0.1), mgp = c(1.5, 0.5, 0))
plot(msMat, mark_knots = "internal")
 ## derivatives of M-splines
dmsMat <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 2,
intercept = TRUE, derivs = 1)
## or using the deriv method
dmsMat1 <- deriv(msMat)
stopifnot(all.equal(dmsMat, dmsMat1, check.attributes = FALSE))
### periodic M-splines
x <- seq.int(0, 3, 0.01)
bknots <- c(0, 1)
pMat <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 3, intercept = TRUE,
Boundary.knots = bknots, periodic = TRUE)
## integrals
iMat <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 3, intercept = TRUE,
Boundary.knots = bknots, periodic = TRUE, integral = TRUE)
## first derivatives by "derivs = 1"
dMat1 <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 3, intercept = TRUE,
Boundary.knots = bknots, periodic = TRUE, derivs = 1)
## first derivatives by using the deriv() method
dMat2 <- deriv(pMat)
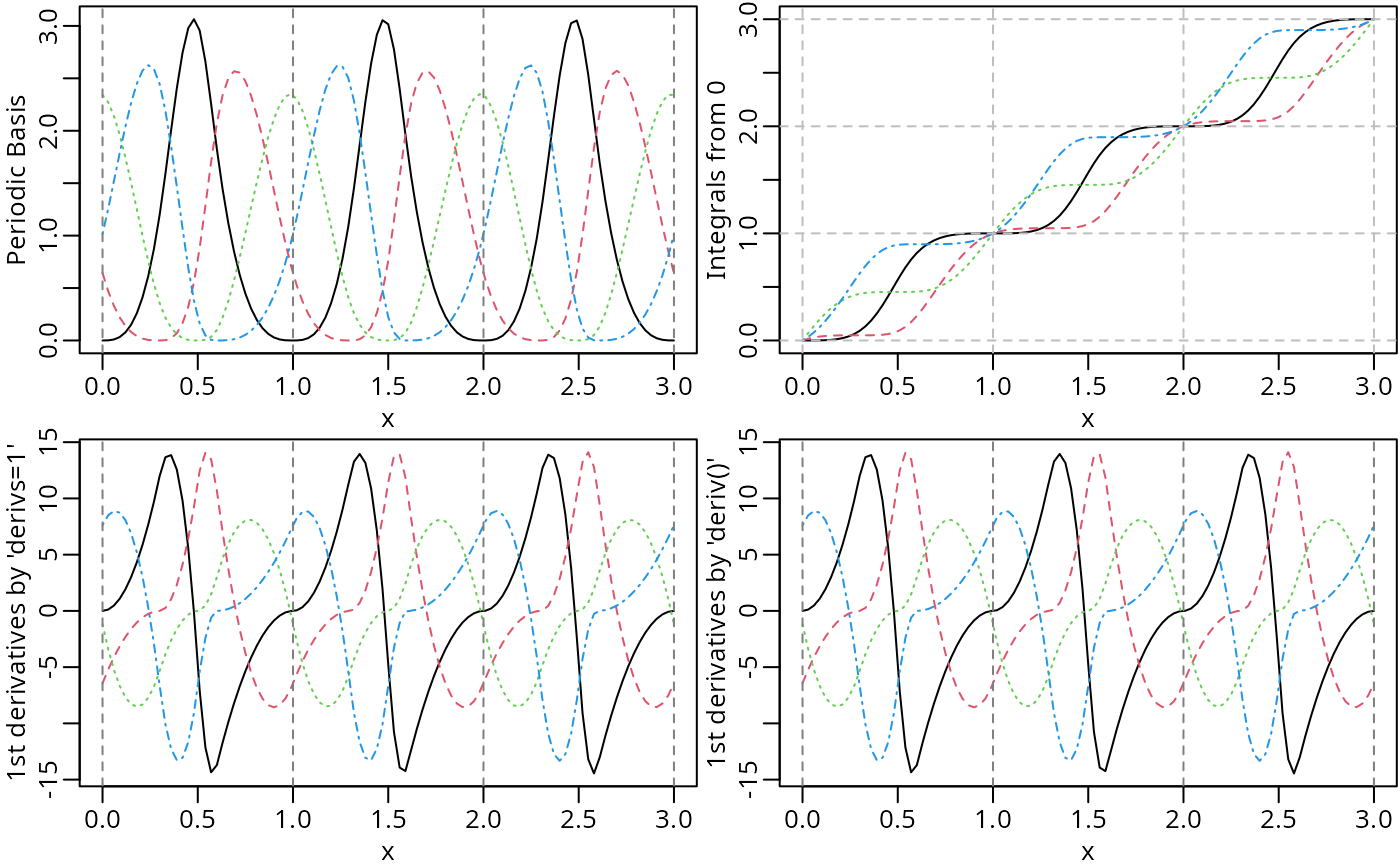
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
plot(pMat, ylab = "Periodic Basis", mark_knots = "boundary")
plot(iMat, ylab = "Integrals from 0")
abline(v = seq.int(0, max(x)), h = seq.int(0, max(x)), lty = 2, col = "grey")
plot(dMat1, ylab = "1st derivatives by 'derivs=1'", mark_knots = "boundary")
plot(dMat2, ylab = "1st derivatives by 'deriv()'", mark_knots = "boundary")
## derivatives of M-splines
dmsMat <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 2,
intercept = TRUE, derivs = 1)
## or using the deriv method
dmsMat1 <- deriv(msMat)
stopifnot(all.equal(dmsMat, dmsMat1, check.attributes = FALSE))
### periodic M-splines
x <- seq.int(0, 3, 0.01)
bknots <- c(0, 1)
pMat <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 3, intercept = TRUE,
Boundary.knots = bknots, periodic = TRUE)
## integrals
iMat <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 3, intercept = TRUE,
Boundary.knots = bknots, periodic = TRUE, integral = TRUE)
## first derivatives by "derivs = 1"
dMat1 <- mSpline(x, knots = knots, degree = 3, intercept = TRUE,
Boundary.knots = bknots, periodic = TRUE, derivs = 1)
## first derivatives by using the deriv() method
dMat2 <- deriv(pMat)
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
plot(pMat, ylab = "Periodic Basis", mark_knots = "boundary")
plot(iMat, ylab = "Integrals from 0")
abline(v = seq.int(0, max(x)), h = seq.int(0, max(x)), lty = 2, col = "grey")
plot(dMat1, ylab = "1st derivatives by 'derivs=1'", mark_knots = "boundary")
plot(dMat2, ylab = "1st derivatives by 'deriv()'", mark_knots = "boundary")
 par(op) # reset to previous plotting settings
### default placement of internal knots for periodic splines
default_knots <- function(x, df, intercept = FALSE,
Boundary.knots = range(x, na.rm = TRUE)) {
## get x in the cyclic interval [0, 1)
x2 <- (x - Boundary.knots[1]) %% (Boundary.knots[2] - Boundary.knots[1])
knots <- quantile(x2, probs = seq(0, 1, length.out = df + 2 - intercept))
unname(knots[- c(1, length(knots))])
}
df <- 8
degree <- 3
intercept <- TRUE
internal_knots <- default_knots(x, df, intercept)
## 1. specify df
spline_basis1 <- mSpline(x, degree = degree, df = df,
periodic = TRUE, intercept = intercept)
## 2. specify knots
spline_basis2 <- mSpline(x, degree = degree, knots = internal_knots,
periodic = TRUE, intercept = intercept)
all.equal(internal_knots, knots(spline_basis1))
#> [1] TRUE
all.equal(spline_basis1, spline_basis2)
#> [1] TRUE
par(op) # reset to previous plotting settings
### default placement of internal knots for periodic splines
default_knots <- function(x, df, intercept = FALSE,
Boundary.knots = range(x, na.rm = TRUE)) {
## get x in the cyclic interval [0, 1)
x2 <- (x - Boundary.knots[1]) %% (Boundary.knots[2] - Boundary.knots[1])
knots <- quantile(x2, probs = seq(0, 1, length.out = df + 2 - intercept))
unname(knots[- c(1, length(knots))])
}
df <- 8
degree <- 3
intercept <- TRUE
internal_knots <- default_knots(x, df, intercept)
## 1. specify df
spline_basis1 <- mSpline(x, degree = degree, df = df,
periodic = TRUE, intercept = intercept)
## 2. specify knots
spline_basis2 <- mSpline(x, degree = degree, knots = internal_knots,
periodic = TRUE, intercept = intercept)
all.equal(internal_knots, knots(spline_basis1))
#> [1] TRUE
all.equal(spline_basis1, spline_basis2)
#> [1] TRUE